Journal Publications
Full citation data: Pubmed, Web of Science, Google Scholar
† equal contribution | ‡ co-corresponding author
-
- Zamat A†, Kim C†, Sridhar S, Fabrega S, Sen R, Campbell N, Oliver SA, Zha Z, Thiveaud C, Kulaksizoglu E, Brienen M, Okada H, Woodworth G, Arvanitis C‡, and Kwong GA‡, “Closed-loop sonothermogenetic control of CAR T cells for metronomic brain cancer therapy” bioRxiv 2025.04.23.650339. [DOI: 10.1101/2025.04.23.650339]
- Serafini CE, Gorti V, Costa PC, Silva Trenkle AD, Kanwar B, Wang B, Wicker B, Kippner LE, LeCompte I, Chen RQ, Joffe B, Li Y, Bowles-Welch AC, Li J, Brown CE, Kwong GA, Balakirsky S, Roy K, and Robles FE, “Label-free in-line characterization of immune cell culture using quantitative phase imaging” submitted (2025).
- Gorti V, Serafini CE, Silva Trenkle AD, McCubbins K, LeCompte I, Kwong GA, and Robles FE, “Non-destructive, high-resolution T cell characterization and subtyping via deep-ultraviolet microscropy” submitted (2025).
- Badarinath NM, Mondal B, Yellman CM, Holland KL, Lee HJ, Phuengkham H, Cazier AP, Son J, Smith JR, Cox JR, Kristof AJ, Haikal YA, Kwong GA, and Blazeck J, “A facile yeast-display approach for antibody mask discovery” submitted (2025).
- Kim M†, Zamat AH†, Cadena M, Thiveaud C, Sen R, Lee J, Kulaksizoglu E, Oliver A, VanderLaan D, Fábrega S, Zha Z, Kubelick KP, Kim J, Kwong GA‡, and Emlianov SY‡, “Anisotropic gold nanoassemblies for multimodal photoacoustic imaging and photothermal control of CAR T cells to enhance monitoring and treatment of heterogenous tumors” submitted (2025).
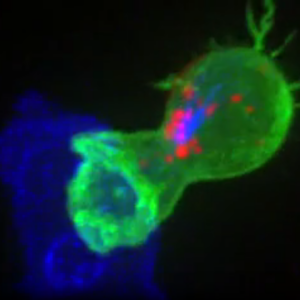
- Gamboa L†, Zamat AH†, Thiveaud CA, Lee HJ, Kulaksizoglu E, Zha Z, Campbell NS, Chan CS, Fábrega S, Oliver SA, Su FY, Phuengkham H, Vanover D, Peck HE, Sivakumar A, Dahotre SN, Harris AM, Santangelo PJ, and Kwong GA, “Sensitizing solid tumors to CAR-mediated cytotoxicity by lipid nanoparticle delivery of synthetic antigens” Nat. Cancer, in press (2025). [DOI: 10.1038/s43018-025-00968-5]
Summary | Most tumors evade recognition by CAR T cell therapies because they closely resemble normal cells. We report the design of synthetic antigens that can be used to tag cancer cells for elimination by CAR T cells modified to target this antigen. We found that this one-two combination proved effective across a wide range of localized solid tumors, providing a promising strategy to treat and manage regional disease before it spreads. 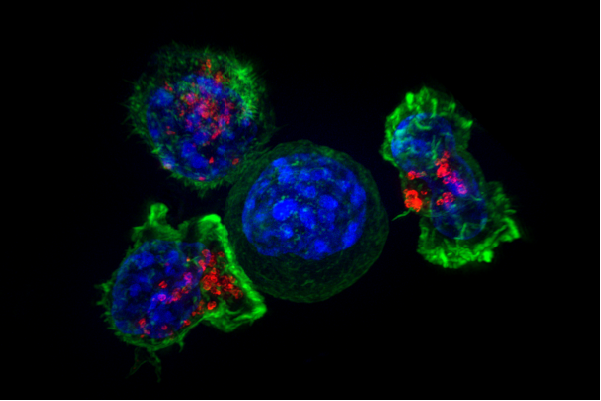
Credit: Alex Ritter, Jennifer Lippincott Schwartz and Gillian Griffiths, National Institutes of Health Press Coverage | Georgia Tech Research News “Painting a Target on Cancer to Make Therapy More Effective” | Time.News | Nipponese News | Futurity | Medical Xpress | Mirage - Sivakumar A, Phuengkham H, Rajesh H, Mac QD, Silva Trenkle AD, Rogers LC, Bawage SS, Hincapie R, Li Z, Vainikos S, Lee I, Xue M, Qiu P, Finn M.G., and Kwong GA, “AND-gated protease-activated nanosensors for programmable detection of anti-tumour immunity” Nat. Nanotechnol. 20, 441–450 (2025). [DOI: 10.1038/s41565-024-01834-8]
Summary | Can computer logic be used to enhance cancer detection? Much like how you need both a username and password to access your account, we engineered biosensors that require multiple biological inputs, happening at the same time, to unlock a detection signal. In preclinical studies, our AND-gated biosensors successfully distinguished between tumors that responded to a common cancer treatment called immune checkpoint blockade and those that did not, even when the immune system was fighting a flu infection. 
Press Coverage | Georgia Tech Research “New Biosensors Could Revolutionize Cancer Detection” | Mirage News | Phys.org | Futurity | Nipponese.news | DPA magazine | Academic Minute
-
- Su FY†, Siebart JC†, Chan CS†, Wang MY, Yao X, Silva Trenkle AD, Sivakumar A, Su M, Harandi R, Shahrawat N, Nguyen CH, Goenka A, Mun J, Dhodapkar MV, and Kwong GA, “Antigen-specific T cell immunotherapy by in vivo mRNA delivery” bioRxiv 2024. [DOI: 10.1101/2024.10.29.620946]
- Gorti V, McCubbins K, Houston D, Silva Trenkle AD, Holberton A, Serafini CE, Wood L, Kwong GA, and Robles FE, “Quantifying UV-induced photo-damage for longitudinal live-cell imaging applications of deep-UV microscopy” Biomed. Opt. Express 16, 208–221 (2025). [DOI: 10.1364/BOE.544778]
- Wu Y, Huang Z, Liu Y, He P, Wang Y, Yan L, Wang X, Gao S, Zhou X, Yoon CW, Sun K, Situ Y, Phuong H, Yuan Z, Zhu L, Zhou Q, Zhao Y, Liu T, Kwong GA, Chien S, Liu L, and Wang Y. “Ultrasound control of genomic regulatory toolboxes for cancer immunotherapy” Nat. Commun. 15, 10444 (2024). [DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54477-7]
- Siebart JC†, Chan CS†, Yao X, Su FY, and Kwong GA, “In vivo gene delivery to immune cells” Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 88, 103169 (2024). [DOI: 10.1016/j.copbio.2024.103169]
- Hua X, Han K, Mandracchia B, Radmand A, Liu W, Kim H, Yuan Z, Ehrlich SM, Li K, Zheng C, Son J, Silva Trenkle AD, Kwong GA, Zhu C, Dahlman JE, and Jia S, “Light-field flow cytometry for high-resolution, volumetric, and multiparametric 3D single-cell analysis” Nat. Commun. 15, 1975 (2024). [DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46250-7]
- Kinney BLC, Gunti S, Kansal V, Parrish CJ, Saba NF, Teng Y, Henry MK, Su FY, Kwong GA, and Schmitt NC, “Rescue of NLRC5 expression restores antigen processing machinery in head and neck cancer cells lacking functional STAT1 and p53” Cancer Immunol Immunother 73, 10 (2024). [DOI: 10.1007/s00262-023-03589-y]
-
- Son J, Mandracchia B, Silva Trenkle AD, Kwong GA, and Jia S. “Portable light-sheet optofluidic microscopy for 3D fluorescence imaging flow cytometry” Lab-on-a-chip 23, 624–630 (2023). [DOI: 10.1039/D2LC01024K]
-
- Holt BA†, Lim HS†, Sivakumar A, Phuengkham H, Su M, Tuttle M, Liakakos H, Qiu P‡, and Kwong GA‡, “Embracing enzyme promiscuity with activity-based compressed biosensing” Cell Reports Methods 3, 100372 (2022). [DOI: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2022.100372]
- Su FY, Zhao QY, Dahotre SD, Gamboa L, Bawage SS, Silva Trenkle AD, Zamat A, Phuengkham H, Ahmed R, Santangelo P, and Kwong GA, “In vivo mRNA delivery to virus-specific T cells by light-induced ligand exchange of MHC class I antigen-presenting nanoparticles” Sci. Adv. 8: eabm7950 (2022). [DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abm7950]
- Mac QD†, Sivakumar A†, Phuengkham H, Xu C, Bowen JR, Su FY, Stentz SZ, Sim H, Harris AM, Li TT, Qiu P, and Kwong GA, “Urinary detection of early responses to checkpoint blockade and of resistance to it via protease-cleaved antibody-conjugated sensors” Nat. Biomed. Eng. 6, 320–324 (2022). [DOI: doi.org/10.1038/s41551-022-00852-y]
Summary | Since 2014, the FDA has approved 7 immune checkpoint inhibitors, but not all patients benefit from therapy. We developed a new class of immune checkpoint inhibitor that is attached with protease sensors for early detection of drug treatment. In preclinical studies, we found that these therapeutic sensors can indicate early responses before future changes in tumor volume, and can identify different types of resistance as they emerge. 
Press Coverage | Georgia Tech Research “Kwong lab develops biosensors for quick assessment of cancer treatment” | Inside Precision Medicine “Biosensors created to detect early response to immune checkpoint blockade” | MedicalXpress | Technology.org | EurekAlert! | ScienMag | Newswise | Bioengineer.org | The Medical News | Technology Networks | ecancer | News-Medical.Net - Holt BA, Tuttle M, Xu Y, Su M, Roise JJ, Wang X, Murthy N and Kwong GA, “Dimensionless parameter predicts bacterial prodrug success” Mol. Syst. Biol. 18: e10496 (2022). [DOI: 10.15252/msb.202110495]
-
- Cazanave SC, Warren AD, Pacula M, Touti F, Zagorska A, Gural N, Huang EK, Sherman S, Cheema M, Ibarra S, Serer A, Bates J, Billin AN, Liles JT, Budas GR, Breckenridge DG, Tiniakos D, Ratziu V, Daly AK, Govaere O, Anstee QM, Gelrud L, Luther J, Chung RT, Corey KE, Winckler W, Bhatia SN, and Kwong GA, “Peptide-based urinary monitoring of fibrotic non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by mass barcoded activity-based sensors” Sci. Transl. Med. 13, eabe8939 (2021). [DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abe8939]
Summary | Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a type of fatty liver disease that has been dubbed the silent epidemic as it has few symptoms. When left undiagnosed and untreated, the liver can develop cirrhosis or liver cancer. We developed synthetic biomarkers to diagnosis NASH early, monitor changes in disease severity, and indicate response to treatment.
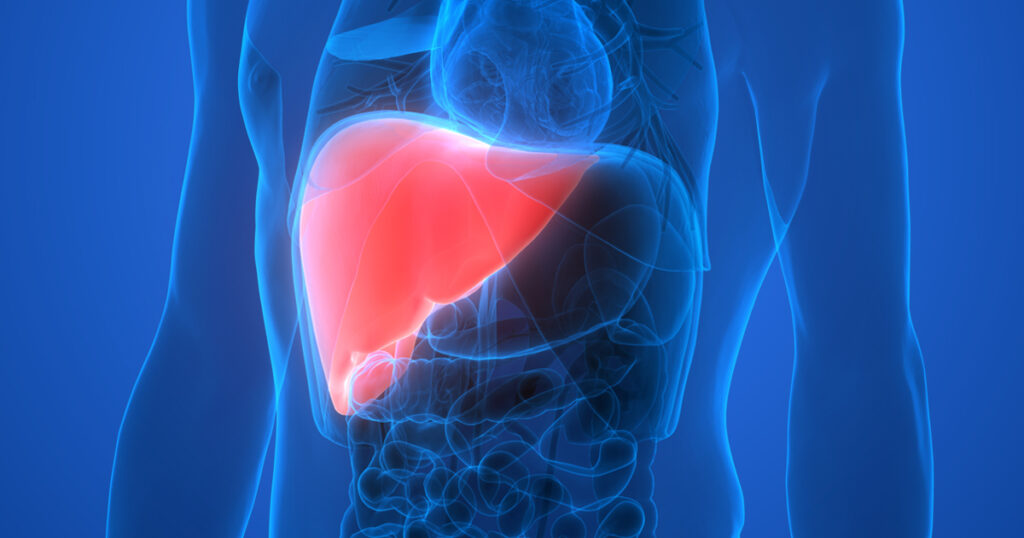
- Miller IC†, Zamat A†, Sun LK, Phuengkham H, Harris AM, Gamboa L, Yang J, Murad JP, Priceman SJ and Kwong GA, “Enhanced intratumoural activity of CAR T cells engineered to produce immunomodulators under photothermal control” Nat. Biomed. Eng. 5, 1348–1359 (2021). [DOI: 10.1038/s41551-021-00781-2]
Summary | Treating solid tumors with chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells typically results in poor responses. In this study, we developed a new class of CAR T cells that are switched on by localized heating to release potent biologics that are otherwise too toxic to use systemically. Thermal targeting of CAR T cells opens the door for spatial control to potentiate cancer therapy.
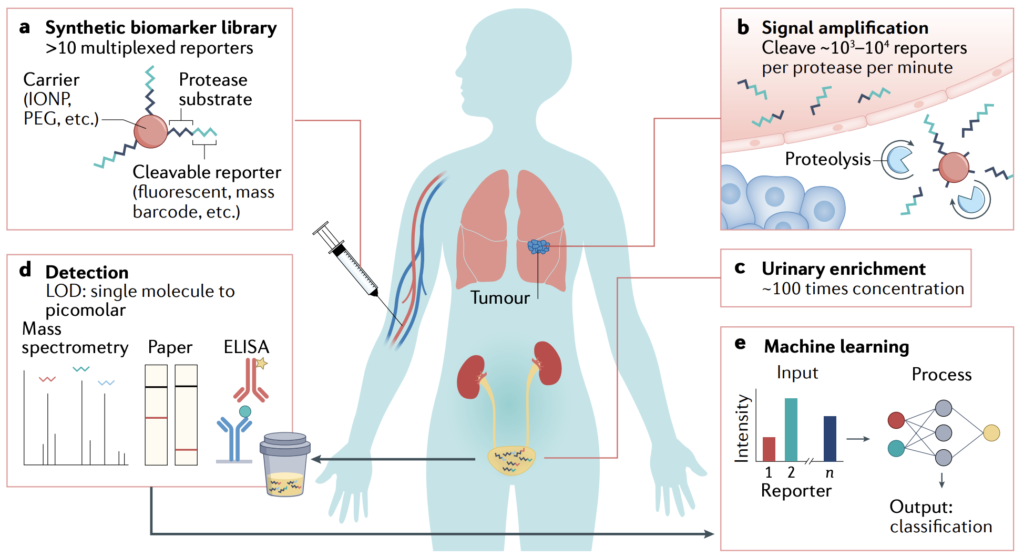
Press Coverage | Georgia Tech Research Horizons “Heat-controllable CAR T-cells destroy tumors and prevent relapse in new study” | TheScientist “Heating up CAR T cells for cancer therapy” | GEN “CAR T gets hot under the collar for cancer targets” | Inside Precision Medicine “CAR T cell modifications show improvement for treating solid tumors” | Newswise | MedicalXpress | The Medical News | Technology Networks | AZO Life Sciences | Front Line Genomics | Science Daily | The Science Advisory Board | BioSpace - Kwong GA‡, Ghosh S, Gamboa L, Patriotis C, Srivastava S‡, and Bhatia SN‡, “Synthetic Biomarkers: A 21st century path to early cancer detection” Nat. Rev. Cancer 21, 655–668 (2021). [DOI: 10.1038/s41568-021-00389-3]
Summary | In 2019, the NCI Division of Cancer Prevention co-organized a think tank meeting on synthetic biomarkers for early detection. We wrote this review to summarize the current science and as a clarion call for more scientists and engineers to work together to solve this important problem. We also dedicated the article to the late Dr. Sam Gambhir, a visionary pioneer and thought leader in bioengineering who devoted his career to developing methods for early disease detection.
- Bazrafshan A, Kyriazi ME, Holt BA, Deng W, Piranej S, Su H, Hu Y, El-Sagheer A, Brown T, Kwong GA, Kanaras A, and Salaita K, “DNA gold nanoparticle motors demonstrate processive motion with bursts of speed up to 50 nm per second” ACS Nano 15(5), 8427–8438 (2021). [DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.0c10658]
- Su FY†, Mac QD†, Sivakumar A, and Kwong GA, “Interfacing biomaterials with synthetic T cell immunity” Adv. Healthcare Mater. 10, 2100157 (2021). [DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202100157]
- Dahotre SN†, Romanov A†, Su FY, and Kwong GA, “Synthetic antigen-presenting cells for adoptive T cell therapy” Adv. Therap. 4, 2100034 (2021). [DOI: 10.1002/adtp.202100034]
-
- Turner TC†, Sok MCP†, Hymel LA†, Pittman F, York WY, Mac QD, Vishna S, Lim HS, Kwong GA, Qiu P, and Botchwey EA, “Harnessing lipid signaling pathways to target specialized pro-angiogenic neutrophil subsets for regenerative immunotherapy” Sci. Adv. 6(44), eaba7702 (2020). [DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aba7702]
- Holt BA and Kwong GA, “Protease circuits for processing biological information” Nat. Commun. 11, 5021 (2020). [DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-18840-8]
Summary | Biological circuits engineered to interface with living systems will enable new applications for programmable immune therapies and diagnostics. In this study, we explored how treating proteases as ‘biological bits’ could be used to design cell-free biocircuits with the capacity to perform digital operations such as analog-to-digital conversion for drug delivery, as well as analog operations that implement ‘fuzzy logic’ to solve mathematical problems.
Press Coverage | Georgia Tech Research Horizons “‘Programmable Medicine’ is the goal for new bio-circuitry research” | Phys.org | Mirage News | TMR Blog - Gamboa L†, Zamat A† and Kwong GA, “Synthetic immunity by remote control” Theranostics 10(8): 3652–3667 (2020). [DOI: 10.7150/thno.41305]
- Kwong GA, “Macrophage sensors for early cancer detection” Clin. Chem. 66(2), 268–270 (2020). [DOI: 10.1093/clinchem/hvz017]
- Tadros AR, Romanyuk A, Miller IC, Santiago A, Noel RK, O’Farrell L, Kwong GA and Prausnitz MR, “STAR particles for enhanced topical drug and vaccine delivery” Nat. Med. 26, 341–347 (2020). [DOI:10.1038/s41591-020-0787-6]
- Gamboa L, Phung EV, Li H, Meyers JP, Miller IC and Kwong GA, “Heat-triggered remote control of CRISPR-dCas9 for tunable transcriptional modulation” ACS Chem. Biol. 15(2), 533–542 (2020). [DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.9b01005]
 Summary | CRISPR-based approaches have achieved wide success in modulating gene activity to control cell function and are potential tools for clinical therapies. However, the lack of precise methods to deliver and control Cas protein expression in vivo remains a critical hurdle. Here we develop a tunable, heat-triggered platform that regulates mammalian cell transcription by remote control of dCas9 transcriptional modulators.
Summary | CRISPR-based approaches have achieved wide success in modulating gene activity to control cell function and are potential tools for clinical therapies. However, the lack of precise methods to deliver and control Cas protein expression in vivo remains a critical hurdle. Here we develop a tunable, heat-triggered platform that regulates mammalian cell transcription by remote control of dCas9 transcriptional modulators.